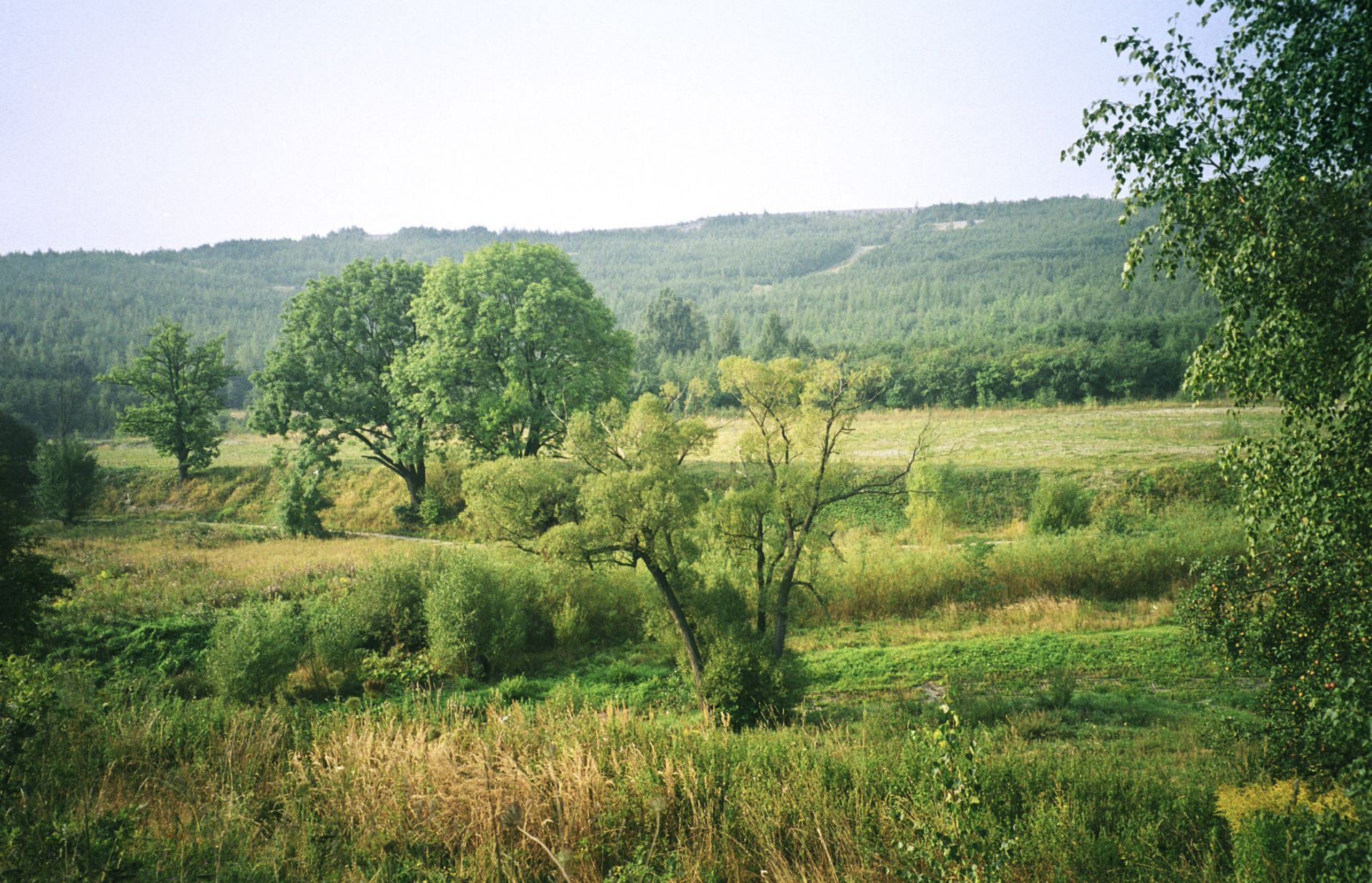

The assumptions of the Environmental Policy regarding the circular economy are implemented along the value chain through the rational use of environmental resources such as land, water, and forests; responsible management of natural raw materials; reduction of waste generation; continuous improvement of waste management techniques; and the closing of water and wastewater circularities.
These principles are reflected, among others, in the PGE CG’s sustainable procurement practices, which promote innovative solutions – especially those that enhance internal processes through automation – as well as technologies that reduce environmental impact.
A dedicated Circular Economy segment has been established within the PGE CG. It is responsible for promoting, developing, and implementing circular economy principles across the organisation, as well as for increasing the use of waste and materials involved in the generation of electricity and heat. This initiative addresses the challenges faced by the Polish economy in both the near term and long-term transformation.
The leading role within this segment is held by PGE Ekoserwis S.A., the Group company designated to carry out circular economy tasks. Its strategy focuses on ensuring the Group’s operational efficiency by maintaining continuity in the collection of combustion waste from energy generation and maximising its reuse. Within PGE Ekoserwis S.A., specific units have been established to implement ongoing circular economy activities, including:
- The By-Product Management Division, which handles the collection and processing of waste into either commercial products or waste streams;
- The Business Development and Innovation Division, which ensures operational continuity by monitoring and responding to evolving technical, regulatory, and market conditions.

Activities undertaken by the Circular Economy segment focus on closing the resource loop for materials such as waste, by-products of combustion from the generation of electricity and heat using hard coal, lignite, and biomass.
Since December 2022, the Circular Economy Research and Development Centre, located in Bełchatów, has served as a key R&D hub responsible for developing and implementing solutions to optimise the reuse of industrial waste from the energy sector and the recycling of materials from decommissioned RES installations. The Center plays a vital role as a concentration point for the Group’s main personnel and laboratory resources in the field of circular economy.
Its ongoing scope of activity includes, in particular:
- research and development initiatives;
- laboratory tests related to product quality control and R&D initiatives;
- overseeing the quality of goods and materials placed on the market;
- collaborating with external entities, including research institutions;
- supporting PGE CG companies in evaluating and developing existing and innovative technologies in the area of circular economy;
- managing matters related to patent protection for technological and material solutions developed at the Centre.

In line with the waste hierarchy and circular economy principles, priority is given to preventing waste generation. One key initiative in this area is obtaining administrative decisions confirming that certain types of waste qualify as by-products. As a result of the company’s efforts, the majority of waste and combustion by-products are transferred to authorised external recipients for further industrial use.

Current and planned initiatives coordinated by PGE Ekoserwis S.A. concerning inbound and outbound resource flows and waste include:
- The Group operates a post-mining coal recovery plant (Zower sp. z o.o.). The project has expanded the application of the aggregate produced at the plant, including its partial use in road construction mixtures, thereby reducing reliance on natural aggregates.
- A new installation method is being introduced at PGE Energia Odnawialna for PV farm projects, involving the use of ballast components for mounting ground-based photovoltaic systems. This is especially important for industrial sites where traditional support structures are difficult to implement.
- Work is ongoing to develop a special additive for rubber materials based on combustion by-products, offering a viable alternative to natural or synthetic raw materials.
- Efforts are underway to develop a technology for processing wind turbine blades into materials that can be reused in other industries. Wind farms currently under construction in Poland are expected to be decommissioned in approximately 25 years. The blades, mostly made of materials that may become difficult to recycle in the future, are the focus of these efforts.
- Production of synthetic gypsum at flue gas desulphurisation (FGD) units of Bełchatów, Opole, Turów, Dolna Odra and Rybnik Power Plants. The generation of synthetic gypsum is the result of a deliberate decision to produce a useful material rather than waste. The choice of desulphurisation technology was based on its ability to yield synthetic gypsum during the FGD process and was an intentional decision made by the plant operator. Moreover, to ensure the highest quality of the final product, the FGD technology is continuously improved and adjusted to reflect changing fuel parameters and increasingly stringent environmental requirements. The expected outcomes have been achieved, with 100% of the synthetic gypsum produced recognised as a product or by-product.
- Production of fly ash and slag as by-products at combustion facilities in the conventional generation and district heating sectors. Their recognition as by-products is based on administrative decisions following compliance with the statutory requirements under the Waste Act. The volume of such recognition increases year by year. In 2024, all fly ash, slag, and synthetic gypsum produced at the Rybnik and Opole Power Plants were classified as by-products.
- Ashes, slags, or ash mixtures that did not meet the criteria to be classified as by-products are used in recovery operations, by filling in areas that have been adversely transformed.
- Circular economy efforts also include oil management. The oil necessary for the proper functioning of hydraulic units is regularly cleaned and treated for reuse. Systems have been implemented to minimise consumption and enable reuse, including oil vapour capture systems, sealed oil trays, and oil separators. Waste generated in the process is sent to companies specialising in recycling or disposal. In some locations, waste heat from block transformers is recovered, using dedicated installations and fed into the district heating network.
- Activities supporting circular economy principles are also carried out by Bestgum Polska sp. z o.o. (a subsidiary of PGE GiEK S.A.), which provides services including maintenance, regeneration, repair, and vulcanisation of conveyor belts and drums (materials provided by the company’s clients); repair of electric motors and transformers; and vulcanisation of conveyor belts.
- Circular Economy practices in the water and wastewater domain included the following measures to reduce the use of water for technological purposes:
- Reusing portions of wastewater and used process water in other technological processes (e.g. reuse of brine from cooling, filtrates, rinse water, and used water from flue gas desulphurisation units, as well as drainage water in the slag removal process),
- Using rainwater for industrial water production and other internal processes,
- Recirculating portions of used water and wastewater for further treatment
and conversion into industrial water.
Waste that could not be recovered due to various factors – such as the scale of generation – is disposed of in landfill sites.
